tests for ovarian torsion|ovarian torsion recovery time : Chinese In one series of 63 patients with suspected torsion, the most sensitive sonographic findings were ovarian edema (sensitivity 85.1 percent and specificity 18.8 percent), abnormal . Informação: A página de placares ao vivo Vitória em Flashscore.com.br oferece placares ao vivo, resultados, classificação de campeonatos e resumos de jogo com artilheiros, cartões amarelos e cartões vermelhos, comparação de odds (cotações de apostas) e estatísticas de confrontos para Vitória. O Live Centre em Flashscore.com.br (disponível para as .
{plog:ftitle_list}
O 777 Casino Clube VIP. Todo o Grupo 888, e isso inclui o 777 Casino, possui um clube VIP com recompensas por fidelidade, promoções VIP, suporte especializado e até eventos especiais. Quem gostou para valer .
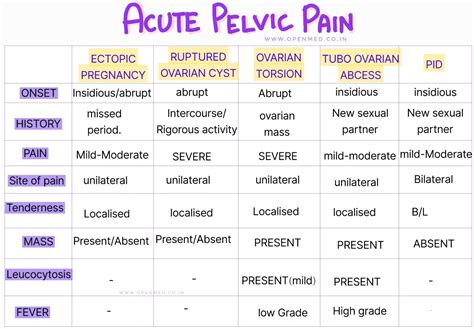
The only way to get a definitive diagnosis, though, is for a surgeon to see the twisted ovary inside your body. Often, they use a procedure called laparoscopy to examine your ovaries directly. If they see ovarian torsion during the laparoscopy, they can treat it right away . CT and MRI are not generally used to diagnose ovarian torsion but are commonly done to rule out other abdominal pathology such as acute appendicitis. The definitive .
Doctors typically begin to think about ovarian torsion based on hearing a patient’s symptoms and conducting a physical examination. An ultrasound (usually a transvaginal one) can confirm the diagnosis. In one series of 63 patients with suspected torsion, the most sensitive sonographic findings were ovarian edema (sensitivity 85.1 percent and specificity 18.8 percent), abnormal .
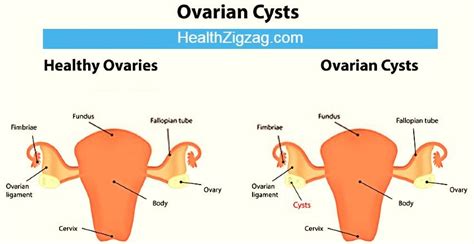
Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary (and/or fallopian tube) on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary. . Ovarian torsion is a surgical emergency. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function where this is clinically appropriate and it is important .
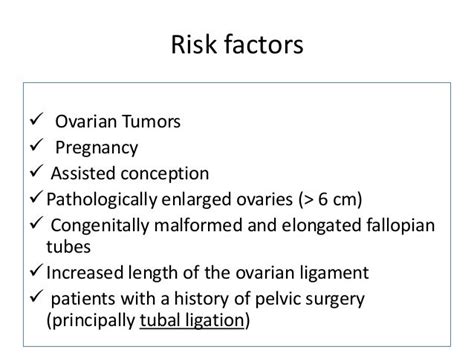
Before testing, they can only rely on a person’s medical history, physical exam, and risk factors for ovarian torsion. There are no specific blood tests that can indicate ovarian torsion. A pelvic ultrasound is the best . Ovarian torsion is a gynaecological emergency: a delay in diagnosis and referral can lead to a reduction in fertility. Ovarian masses are the most common cause of ovarian torsion, but torsion can occur in their absence, .
Pregnancy test: Pregnancy is an ovarian torsion risk factor, so it is useful to confirm it or rule it out. Doppler ultrasound: This test, which can be either transvaginal or .
If you have risk factors for ovarian torsion or your OB-GYN suspects it, they will likely perform medical tests. These may include: Blood tests: The OB-GYN may use this approach to check for an infection or signs of a hemorrhage. Pregnancy test: Pregnancy is an ovarian torsion risk factor, so it is useful to confirm it or rule it out. Doppler ultrasound: This .Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary (and/or fallopian tube) on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function. Ovarian torsion occurs when the ovary rotates around its supporting ligaments, twisting and squashing the accompanying blood vessels and lymphatics.The term adnexal torsion is preferred because a portion of the fallopian tube is commonly torsed along with the ovary.The term adnexal torsion also encompasses rarer entities that do not affect the ovaries .Ovarian torsion (OT) or adnexal torsion is an abnormal condition where an ovary twists on its attachment to other structures, such that blood flow is decreased. [3] [4] Symptoms typically include pelvic pain on one side.[2] [5] While classically the pain is sudden in onset, this is not always the case. [2]Other symptoms may include nausea. [2] Complications may include .
Ovarian torsion (adnexal torsion) is an infrequent but significant cause of acute lower abdominal pain in women. This condition is usually associated with reduced venous return from the ovary as a result of stromal edema, internal hemorrhage, hyperstimulation, or a mass. . Laboratory testing should include a complete blood count (CBC), a .
instrumentation laboratory analyzer distributors wyoming
twisted or ruptured ovarian cyst
Ovarian torsion - Knowledge @ AMBOSS provides information on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of ovarian torsion.A positive pregnancy test does not eliminate the diagnosis of ovarian torsion, especially early in pregnancy, as a corpus luteum cyst may be the source of torsion. Physical exam should include an abdominal exam and a pelvic exam, including a bimanual exam, to assess for adnexal tenderness and fullness that may be present.
Ovarian torsion happens when your ovaries — and sometimes the fallopian tube — twist around the tissue they’re connected to. This cuts off the blood supply to your ovaries, which can cause . Adnexal torsion is the twisting of the ovary, and often of the fallopian tube, on its ligamental supports, resulting in vascular compromise and ovarian infarction. The definitive management is surgical detorsion, and prompt diagnosis facilitates preservation of the ovary, which is particularly important because this condition predominantly affects premenopausal .Performing a urine pregnancy test or beta human chorionic gonadotropin test is an important first step for sexually active, premenopausal patients. . ruptured ovarian cyst, adnexal torsion, and .
Ovarian torsion is a gynaecological emergency characterised by the ovary twisting or torting on the ligaments that suspend it within the pelvis. While the exact incidence is unknown, it accounts for 2-3% of all acute gynaecological emergencies.1 In torsion, the ovary typically twists around the infundibulo-pelvic ligament, also known as the .
The fallopian tube often twists along with the ovary; when this occurs, it is referred to as adnexal torsion or tubo-ovarian torsion.. The condition can be acute, intermittent or sustained (i.e chronic). Ovarian torsion is a difficult diagnosis to make. US, CT or MRI scanning can assist in diagnosis, but ovarian torsion may ultimately have to be a clinical diagnosis in .The overall recurrence rate of ovarian torsion is low, ranging from 2% to 12%; although, reportedly, the rate is higher in spontaneously torsed normal adnexa 48 8. Oophoropexy is controversial and current data are insufficient to support performing an oophoropexy to decrease the risk of recurrent ovarian torsion 47 13 44.This leaflet is to help you understand what an Ovarian torsion is, what tests you need and the implication of being diagnosed for you and your baby. What is the ovarian torsion? Ovarian torsion (also known as adnexal torsion) is considered a surgical emergency. It occurs when there is rotation of the adnexal supporting structures around their .
Ovarian torsion. Cysts can grow so big that they distort the shape of your ovary, increasing the likelihood that it’ll twist. The twisting can prevent blood flow to your ovary, causing it to die. . Then, they may use the following tests to diagnose an ovarian cyst: Advertisement. A pelvic exam: Your provider will feel inside your pelvis for . Ovarian torsion is defined as partial or complete rotation of the ovarian vascular pedicle and causes obstruction to venous outflow and arterial inflow. Ovarian torsion is usually associated with a cyst or tumor, which is .
Ovarian torsion is the rotation of the ovary and portion of the fallopian tube on the supplying vascular pedicle; Referred to as adnexal torsion and tubo-ovarian torsion; Occurs in females of all ages Most common in reproductive age .
The identification of ovarian torsion relies on tests developed for the diagnosis of various forms of abdominal pain. These include: Pelvic exam: A pelvic exam can help a physician determine your pain’s point of origin. Urine test: Urine tests document evidence of infection and also rule out pregnancy as a cause of symptoms. Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary (and/or fallopian tube) on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function. Most often seen in women of reproductive age be.
risk factors for ovarian torsion
Clinical history is vital in the diagnosis of an adnexal mass (). 4 Risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. The patient's reproductive status and contraception method must be determined .How is ovarian torsion diagnosed? A doctor may use the following tests to diagnose ovarian torsion: Transvaginal ultrasound: This requires inserting a small instrument called a probe into the vagina. Abdominal ultrasound: This uses an ultrasonic probe on the outside of the belly.Testicular torsion causes your testicle to twist and cuts off its blood supply. It causes severe pain and requires emergency care. . What tests will be done to diagnose testicular torsion? Your healthcare provider may order a scrotal ultrasound to determine if blood is flowing within your testicular tissues. A scrotal ultrasound is a quick .
Ovarian torsion (adnexal torsion) is an infrequent but significant cause of acute lower abdominal pain in women. . Beyond the Basics: Test Your Knowledge of Predictive Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer 0.25 LOC / CME Credits education. You are being redirected to Medscape Education Yes, take me there. 0.25 LOC / CME. Beyond the Basics: Test Your . ovarian torsion. It occurs in 86% to 95% of all cases of torsion and is more common in masses measuring greater than 5 cm.1 These masses are usually benign in nature, but a malignant mass can be involved, and, if involved, is more common in postmenopausal women with ovarian torsion. Treatment Once ovarian torsion is highly suspected or . OBJECTIVE. The CT and MRI features of ovarian torsion are illustrated with gross pathologic correlation. Ovarian enlargement with or without an underlying mass is the finding most frequently associated with torsion, but it is nonspecific. A twisted pedicle, although not often detected on imaging, is pathognomonic when seen. Subacute ovarian hemorrhage . Ovarian torsion—also known as a twisted ovary or torsed ovary—is a rare but serious condition that mainly affects people of reproductive age (15–45 years). . seen on an imaging test of a .
Pelvic adnexal torsion is a collective term referring to twisting of an ovary, fallopian tube, or paraovarian cyst on its axis with varying degrees of vascular compromise. Although it is the fifth most common gynecologic emergency, the diagnosis is challenging and often missed due to symptoms, physical examination findings, and imaging features that are nonspecific. Delay .
instrumentation laboratory analyzer maintenance
Teresa Mary Palmer (born 26 February 1986) is an Australian actress. She began her career with roles in Bedtime Stories (2008), The Sorcerer's Apprentice (2010), Take Me Home Tonight (2011), and I Am Number Four (2011). She received further recognition for starring in the films Warm Bodies (2013), Lights Out (2016), Hacksaw Ridge (2016), and Berlin Syndrome (2017). She also starre.
tests for ovarian torsion|ovarian torsion recovery time